
Your chest often defines your masculinity and enlarged breast tissue can impact your confidence. Many men assume they have gynecomastia when they notice chest changes. However, there are many causes of gynecomastia and an incorrect diagnosis may lead to the wrong treatment.
Pseudogynecomastia is a condition that involves excess fat accumulation, not enlarged breast glands like true gynecomastia. Fat behaves differently than gland tissue. It responds to different treatments. Understanding this difference determines whether the treatment chosen will be successful.
Learn About: What Makes a Men Tummy Tuck Different?
Definition and Characteristics of Pseudogynecomastia
Pseudogynecomastia represents a condition where excess fat tissue accumulates in the chest area, creating the appearance of enlarged breasts. This differs fundamentally from true gynecomastia, which involves actual breast gland tissue growth.
In all men, the chest area contains both fat tissue and small amounts of breast gland tissue. When fat tissue increases significantly, it can create a feminine chest appearance that may cause emotional distress. This excess fat typically distributes evenly across the chest area. Gland tissue tends to concentrate directly behind the nipple.
Men with pseudogynecomastia often notice their chest tissue feels soft and moveable when pressed. The tissue lacks the firm, rubbery texture associated with enlarged breast glands. Understanding these physical differences helps both patients and medical professionals identify the type of gynecomastia present.
The appearance of pseudogynecomastia can vary significantly between individuals:
- Some men experience mild chest fullness
- Others develop pronounced breast-like contours
- Severity often correlates with overall body fat percentage
- Genetics influence individual fat distribution patterns
Causes of Pseudogynecomastia

Multiple factors contribute to pseudogynecomastia development with most cases involving a combination of influences rather than a single cause.
Excess Body Fat Accumulation
Weight gain represents the most common cause of pseudogynecomastia. As men gain weight, fat tissue accumulates throughout the body, including the chest area. Some men naturally store more fat in their chest region due to genetic factors.
The chest area may be a primary fat storage location for many men, particularly those with certain body types. This tendency can persist even when other body areas remain relatively lean. Men who gain weight rapidly often notice chest changes before fat accumulation becomes obvious elsewhere.
Age-related metabolism changes also contribute to chest fat accumulation. Men typically experience slower metabolism after age 30, making weight management more challenging. Hormonal changes that occur with aging can also influence where the body stores fat tissue.
Hormonal Imbalances (e.g., low testosterone)
Testosterone levels play a significant role in male body composition and fat distribution. Low testosterone can lead to increased fat storage, particularly in areas like the chest, abdomen, and hips. This hormonal imbalance often develops gradually, making changes less noticeable initially.
Estrogen levels also influence chest fat accumulation in men:
- When estrogen levels rise relative to testosterone, fat storage patterns shift
- This can occur naturally with aging
- The result often includes more feminine fat distribution patterns
Insulin resistance represents another hormonal factor that contributes to chest fat accumulation. Men with insulin sensitivity issues often experience difficulty losing fat from specific body areas, including the chest region. This makes traditional weight loss approaches less effective for addressing pseudogynecomastia.
Certain Medications (e.g., steroids, antidepressants)
Various medications can contribute to pseudogynecomastia development through different mechanisms. Corticosteroids, commonly prescribed for inflammatory conditions, can cause significant weight gain and alter fat distribution patterns.
Antidepressants, particularly certain classes like SSRIs, may influence weight gain and fat storage. Many patients notice chest changes after starting these medications, especially when combined with decreased physical activity levels.
Anabolic steroids, used both medically and recreationally, can create complex hormonal changes that affect chest tissue composition. These substances can influence both fat accumulation and gland tissue development, sometimes creating mixed presentations.
Pseudogynecomastia vs. Gynecomastia
Understanding the fundamental differences between these conditions is important for proper treatment planning and realistic outcome expectations.
Identifying Fat Tissue vs. Gland Tissue
Fat tissue feels soft, moveable, and distributes evenly across the chest area. When pressed, it compresses easily and lacks distinct borders or edges. Men can often feel the difference by comparing their chest tissue to fat in other body areas.
Gland tissue presents as firm, sometimes tender masses typically located directly behind the nipple area. This tissue feels more rubbery or dense compared to fat and often has more defined borders. Gland tissue may also cause nipple sensitivity or slight discharge in some cases.
The pinch test provides a simple way to assess tissue type:
- Grasping chest tissue between fingers reveals tissue composition
- Fat tissue pinches easily and feels soft
- Gland tissue feels more resistant and substantial
- This basic test helps distinguish between the two types
Mixed presentations occur frequently, where men have both excess fat and gland tissue enlargement. These cases require careful evaluation to determine the main component of the gynecomastia, whether it is fat or gland tissue, and allow appropriate planning of treatment options.
The Role of Body Mass Index (BMI)
Men with higher BMI values more commonly develop pseudogynecomastia, as excess weight correlates directly with increased fat storage throughout the body. However, even men within normal weight ranges can experience chest fat accumulation due to genetic predisposition.
Body fat percentage provides more information than BMI alone for assessing pseudogynecomastia. Men with body fat percentages above 20% often notice more pronounced chest changes, regardless of their overall weight classification.
Muscle mass also influences chest appearance significantly. Men with well-developed chest muscles may notice less apparent chest fat, as muscle tissue provides better underlying support and definition. Conversely, men with limited muscle development may find chest fat more noticeable.
The Importance of Hormonal Levels
Testosterone levels directly impact both fat distribution and muscle development patterns. Men with optimal testosterone levels typically maintain leaner chest areas and better overall body composition. Regular monitoring can help identify hormonal contributions to chest changes.
Thyroid function also affects metabolism and fat storage patterns. Hypothyroidism can contribute to weight gain and altered fat distribution, including increased chest fat accumulation. Addressing thyroid issues often improves overall body composition outcomes.
Insulin sensitivity influences how effectively the body processes nutrients and stores fat. Men with better insulin sensitivity typically find fat loss easier and more sustainable, including fat reduction in the chest area.
Symptoms of Pseudogynecomastia
Pseudogynecomastia presents with distinct symptoms that affect both physical appearance and emotional well-being.
Physical Signs
The most obvious sign involves enlarged chest tissue that creates a breast-like appearance. This enlargement typically affects both sides symmetrically, though some asymmetry can occur based on individual fat distribution patterns.
Chest tissue feels soft and compressible when pressed, unlike the firm texture associated with muscle or gland tissue. The affected area may also feel warm or slightly tender, particularly if weight gain occurred rapidly.
Clothing fit changes represent another common symptom:
- Shirts may feel tighter across the chest area
- Certain clothing styles may emphasize the chest enlargement
- Many men choose looser-fitting clothes to minimize appearance
- Shopping for properly fitting clothes can become more challenging
Nipple area changes can also occur with pseudogynecomastia. The surrounding tissue, known as the areola, may have a puffy or protruding appearance that affects overall chest contour.
Emotional Impact on Affected Individuals
Men with pseudogynecomastia may experience emotional distress related to their chest appearance. Many report feeling self-conscious about removing their shirts in public settings like beaches, pools, or locker rooms.
Social situations become challenging when chest appearance affects confidence levels. Many men avoid certain activities or clothing choices that might draw attention to their chest area. This avoidance can limit social interactions and recreational activities.
Intimate relationships may also suffer when men feel embarrassed about their chest appearance. Many report decreased confidence during intimate moments, which can affect relationship satisfaction and personal well-being.
Body image concerns frequently extend beyond the chest area. Men dealing with pseudogynecomastia often develop broader concerns about their overall appearance and fitness levels, leading to decreased self-esteem.
Diagnosis of Pseudogynecomastia
Proper diagnosis requires comprehensive evaluation by a qualified plastic surgeon who understands the differences between various chest conditions.
Physical Examination Techniques
The physical examination begins with visual assessment of chest symmetry, contour, and overall appearance. The plastic surgeon evaluates how the chest tissue appears, noting any asymmetries or unusual features.
Palpation involves carefully feeling the chest tissue to assess texture, density, and distribution patterns. This technique helps distinguish between fat tissue, gland tissue, and normal chest muscle. The examination includes assessment of tissue mobility and firmness.
Compression testing helps evaluate tissue composition by applying gentle pressure to different chest areas:
- Fat tissue compresses easily under pressure
- Gland tissue remains more resistant to compression
- This test provides valuable information about predominant tissue type
- Results help guide treatment planning decisions
Range of motion assessment examines how chest tissue moves during arm movements and position changes. This evaluation helps determine tissue attachment patterns and mobility, which influences treatment planning decisions.
Imaging Tests and Their Relevance
Ultrasound imaging provides detailed views of chest tissue composition without radiation exposure. This non-invasive test can clearly distinguish between fat tissue and gland tissue, helping confirm the diagnosis and guide treatment planning.
Mammography may be recommended in certain cases to rule out any underlying breast tissue abnormalities. While less commonly used for pseudogynecomastia evaluation, it can provide valuable information when the diagnosis remains unclear.
CT or MRI imaging might be considered for complex cases involving significant tissue changes or when surgical planning requires detailed anatomical information. These advanced imaging techniques provide comprehensive tissue analysis.
Blood tests help evaluate hormonal factors that might contribute to chest tissue changes. Testosterone, estrogen, thyroid function, and other hormone levels provide important information about underlying causes and treatment approaches.
Related: What are the Different Types of Gynecomastia?
Treatment Options for Pseudogynecomastia
Treatment options range from conservative lifestyle modifications to surgical interventions depending on severity and individual patient factors.
Lifestyle Changes: Diet and Exercise
Dietary modifications form the cornerstone of pseudogynecomastia treatment for many men. Creating a moderate caloric deficit through balanced nutrition helps reduce overall body fat, including chest area accumulation. Focus on whole foods, lean proteins, and controlled portion sizes.
Cardiovascular exercise helps burn calories and improve overall body composition:
- Activities like running, cycling, or swimming reduce body fat effectively
- Consistency in exercise routine produces the best results
- Aim for 150-300 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise weekly
- Combine different activities to maintain motivation and interest
Strength training, particularly chest-focused exercises, can help improve chest appearance by building underlying muscle tissue. While exercise cannot directly target chest fat loss, improved muscle definition can significantly enhance overall chest contour.
Results from lifestyle changes typically become noticeable after 3 to 6 months of dedicated effort, with continued improvement over time for those who maintain healthy habits.
Minimally Invasive Liposuction Techniques
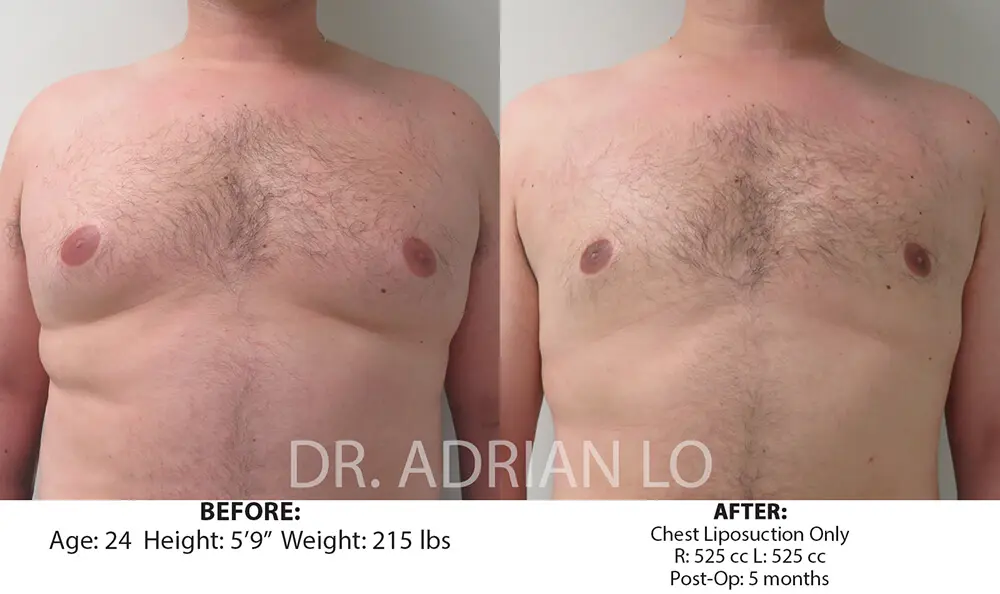
Liposuction represents an effective treatment option for men with excess chest fat that does not respond adequately to lifestyle changes. Modern techniques allow for fat removal with minimal scarring and downtime.
Tumescent liposuction involves injecting a solution containing local anesthetic and epinephrine to minimize bleeding and discomfort. Small incisions allow access for thin cannulas to gently remove excess fat tissue while preserving important structures.
Ultrasonic liposuction is another useful liposuction technique that uses ultrasonic waves to “melt’’ the fat that forms pseudogynecomastia.
Power-assisted liposuction uses specialized equipment to break up fat tissue more efficiently, allowing for smoother results and potentially shorter procedure times. This technique works particularly well for fibrous chest fat that might be more difficult to remove.
Recovery from chest liposuction typically involves wearing a compression garment for four weeks to support healing and optimize results. Most men return to normal activities within one week, with full results visible after swelling resolves.
Potential Surgical Interventions
Direct surgical excision which is called subcutaneous mastectomy, may be necessary when liposuction alone cannot achieve optimal results. This approach involves making a small incision at the edge of the nipple to remove the gland tissue.
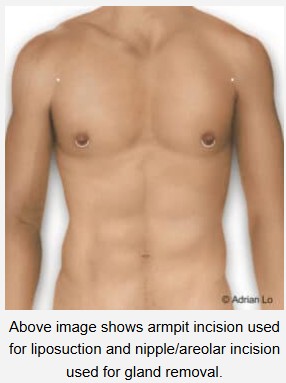
Combination procedures often provide the best results for men with both excess fat and gland tissue. The plastic surgeon can perform liposuction for fat removal and direct excision for gland tissue during the same procedure.
Skin removal procedures might be recommended for men with significant loose skin along with their pseudogynecomastia or for loose skin that might result after fat and gland removal.
- Excess skin can create ongoing chest appearance issues
- Fat or gland removal may not address skin concerns
- Additional surgical correction may be required
- Combined approaches often produce optimal outcomes
Different types of skin removal procedures may be performed at the same time as your pseudogynecomastia procedure. A male breast reduction procedure may be recommended for severe situations.
Related: Surgical Options to Treat Gynecomastia
Managing Expectations During Treatment
Setting appropriate expectations is important for treatment satisfaction and long-term success with any pseudogynecomastia treatment approach.
Realistic Outcomes from Treatment
Non-surgical treatments for chest fat can help men with mild to moderate pseudogynecomastia feel better about their appearance. These treatments can make a big difference, but for many men — especially those who store fat in their chest because of genetics — diet and exercise might not be enough to remove it completely.
Surgical treatments typically provide more dramatic and predictable results than non-surgical approaches. Most men achieve significant improvement in chest contour and overall appearance.
Timeline expectations vary significantly based on treatment approach:
- Lifestyle changes require months to show noticeable results
- Surgical procedures provide immediate improvement
- Results continue to refine over several months as swelling resolves
- Final outcomes may take up to one year to fully appreciate
Individual factors like age, skin quality, muscle development, and overall health status all influence treatment outcomes. Men with good skin elasticity and reasonable muscle tone typically achieve better results than those with significant skin laxity or poor muscle development.
Post-Treatment Care and Advice
Following post-treatment instructions carefully ensures optimal healing and results. This includes wearing compression garments as directed, attending follow-up appointments, and avoiding strenuous activities during the initial recovery period.
Maintaining stable weight after treatment helps preserve results long-term. Significant weight fluctuations can affect chest appearance and potentially compromise treatment outcomes, particularly after surgical procedures.
Regular exercise and healthy eating habits support long-term success regardless of treatment approach. Men who maintain active lifestyles typically experience better overall satisfaction with their results over time.
Ongoing communication with your plastic surgeon helps address any concerns and optimize long-term outcomes. Regular check-ups allow for monitoring of results and early intervention if any issues develop.
Seeking Professional Help for Pseudogynecomastia
Professional evaluation provides the foundation for effective pseudogynecomastia treatment and optimal long-term results.
When to Consult a Specialist
Consider consulting a plastic surgeon when chest appearance concerns affect daily life, clothing choices, or self-confidence. Many men delay seeking help, but early consultation can provide valuable information about treatment options and realistic expectations.
Persistent chest enlargement despite weight loss efforts may indicate the need for medical evaluation. Some men find that even significant weight reduction does not adequately address their chest concerns, suggesting that surgical intervention might be beneficial.
Rapid onset of chest changes or asymmetric development warrants prompt medical evaluation to rule out underlying medical conditions:
- Most cases involve benign fat accumulation
- Sudden changes should be assessed medically as this may indicate breast gland development
- Early evaluation can identify treatable causes
- Reassurance comes from proper medical assessment by a gynecomastia specialist
Age-related chest changes that progressively worsen over time often benefit from medical evaluation. Understanding the underlying causes of gynecomastia helps determine the most appropriate treatment approach for individual circumstances.
Preparing for Your Consultation
Compile a complete medical history including current medications, previous surgeries, lab results and any relevant health conditions. This information helps the plastic surgeon understand potential contributing factors and plan appropriate treatment approaches.
Prepare questions about treatment options, expected results, recovery requirements, and potential risks. Understanding all aspects of available treatments helps you make informed decisions about your care.
Consider bringing photos showing how your chest appearance has changed over time. Visual documentation can help the plastic surgeon understand the progression of your condition and plan optimal treatment methods.
Research the plastic surgeon’s credentials, experience with gynecomastia surgery, before and after pictures and patient reviews. Choosing a qualified plastic surgeon with extensive experience in chest procedures ensures the best possible outcomes.
Get Support for Your Pseudogynecomastia Journey with Dr. Adrian Lo
Dr. Adrian Lo provides specialized care for men dealing with pseudogynecomastia and related chest appearance concerns. His extensive experience with both surgical and non-surgical treatment approaches ensures personalized care that addresses your specific needs and goals.
Understanding the difference between fat tissue and gland tissue is just the beginning of your treatment journey. Dr. Adrian Lo’s comprehensive evaluation process helps determine the most effective treatment approach for your individual situation, whether that involves lifestyle guidance, minimally invasive procedures, or surgical intervention.Contact us today to begin your path toward improved confidence and appearance.
