Surgery can remove gynecomastia , commonly referred to as “gyno” or “man boobs”, but patients often wonder –
Does gynecomastia come back after surgery? Could it return?
This is a valid concern, especially for those who have dealt with the emotional and physical effects of enlarged male breast tissue for years.
Here is the truth: recurrence is uncommon, but not impossible.
It depends on several factors, some you can control, and some you cannot.
Hormones, lifestyle, and surgical technique all play a role.
Knowing how and why gynecomastia might return is the first step toward achieving the long-term results that you desire.
Related: What Causes Man Boobs? From Hormones To Lifestyle Factors
Causes of Gynecomastia or ‘Man Boobs’
A common concern for many patients is, “does gynecomastia come back after surgery,” especially if hormonal changes occur later in life.
The cause of gynecomastia, the enlargement of male breast tissue can be due to many different factors.
Gynecomastia is not just because of weight gain or poor fitness. It commonly involves the growth of firm glandular tissue beneath the nipple area due to hormonal stimulation..
To understand why gynecomastia may or may not return after surgery, it is important to first understand what are the primary causes of breast growth.
Hormonal Imbalances in Adolescents and Adults
The most common cause of gynecomastia is a hormonal imbalance—specifically, between estrogen and testosterone levels in your body.
In adolescent males, temporary gynecomastia is common due to hormonal fluctuations during puberty. While it often resolves on its own, in many cases it persists into adulthood. In older adults, a natural decline in testosterone level can again shift this hormonal balance, resulting in the development of glandular breast tissue.
Use of Anabolic Steroids or Medications
Many medications, including anabolic steroids, anti-androgens, and drugs used for heart disease or mental health conditions, have been associated with gynecomastia.
These medications may elevate estrogen levels or interfere with testosterone production. Even brief exposure to these medications can stimulate breast growth in susceptible individuals.
Underlying Health Conditions Affecting Hormones
Liver disease, thyroid dysfunction, and tumors affecting the adrenal or pituitary glands can lead to hormonal shifts that cause gynecomastia.
When these conditions are untreated, breast tissue growth may recur after gynecomastia surgery.
Therefore, identifying and managing such conditions is important before considering gynecomastia surgery to avoid recurrence.
What Gynecomastia Surgery Involves
Gynecomastia surgery, also known as male breast reduction, is performed to remove excess glandular breast tissue to restore a flat, masculine chest contour.
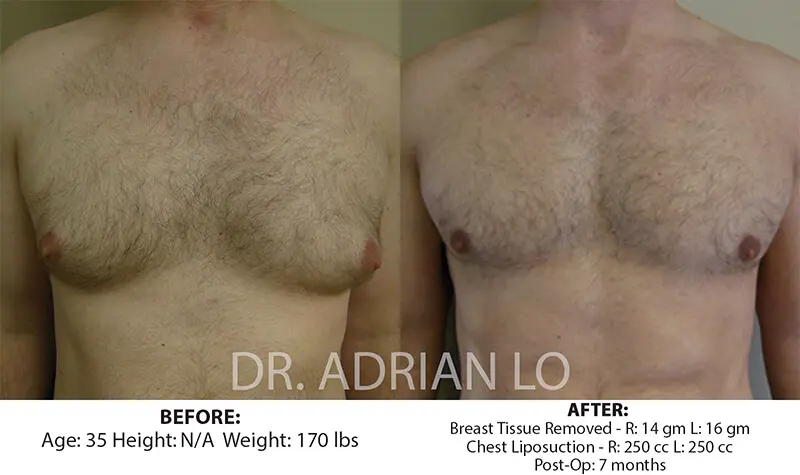
Before undergoing the procedure, most patients want a clear answer to the question: does gynecomastia come back after surgery?
When the procedure is performed correctly by a board-certified plastic surgeon, the results are typically long-lasting and permanent.
Understanding the surgical techniques used helps explain why recurrence is rare but still possible under certain conditions.
Liposuction for Fat Removal in the Chest
Liposuction is frequently used to remove fatty tissue from the chest area.
Liposuction is appropriate for patients whose chest fullness is due to fat deposits rather than true glandular enlargement. However, liposuction alone is insufficient if firm glandular tissue is present, as this tissue does not respond to liposuction and must be excised. Often if liposuction is performed alone for patients that have glandular tissue present, the chest may still have a gynecomastia appearance as the gland tissue remains.
Excision of Glandular Breast Tissue
In patients with true gynecomastia, there is glandular breast tissue and direct surgical removal is required.
This involves making a small surgical incision, typically around the areola, to directly remove the dense glandular tissue beneath. This procedure is called subcutaneous mastectomy and should be performed whenever breast gland tissue is present.
When this breast gland tissue is correctly removed, the likelihood of gynecomastia returning is extremely low.
Combination – Liposuction and Glandular Breast Tissue Removal
Most men with gynecomastia or man boobs have both fatty and glandular enlargement.
In these cases, plastic surgeons use a combination of advanced liposuction and breast gland excision to achieve the desired chest shape.
For more advanced cases, additional techniques such as skin excision may be required to remove loose or stretched skin. This procedure is considered a male breast reduction.
Can Gynecomastia Return After Surgery?
The answer is yes, rarely, but only under specific circumstances.
Gynecomastia does not typically “grow back” if the glandular tissue was fully removed. However, patients may notice the return of a similar appearance if contributing factors are not addressed or if they develop new hormone-related issues.
The risk of gynecomastia returning increases if the patient is exposed to hormone imbalances or if glandular tissue was not fully excised.
Addressing the question—”does gynecomastia come back after surgery”—requires understanding both surgical technique and patient-specific risk factors.
Recurrence Because of Incomplete Gland Removal
In some cases, a portion of the gland tissue may be left behind during surgery due to incomplete removal or to avoid a contour depression in the chest.
This residual breast tissue can be stimulated by hormones and may grow again, leading to the appearance of recurrence. However, it will unlikely be as severe as the first time as there is less breast tissue present that can enlarge or grow.
This is why experience and surgical technique are vital. Choosing a plastic surgeon who specializes in gynecomastia surgery reduces the risk of incomplete removal.
Gynecomastia recurrence after surgery is rare when the gland tissue is completely removed and the patient maintains hormonal stability.
Impact of Hormonal Fluctuations After Surgery
Patients often ask during consultation: does gynecomastia come back after surgery if they maintain a stable hormone profile and healthy lifestyle?
Even after a successful surgery, the body may undergo hormonal changes that reintroduce the conditions which initially caused gynecomastia. This can include natural aging, medication use, or the reintroduction of substances like steroids.
These changes can stimulate the development of new glandular tissue if not properly managed. The primary causes of gynecomastia regrowth include unresolved hormonal imbalances, medication use, or anabolic steroid exposure.
Lifestyle Factors That Influence Recurrence
Patients who resume steroid use, gain a significant amount of weight, or neglect general health may find that their chest contour changes.
A healthy, consistent lifestyle plays a large role in maintaining surgical results. The lifestyle impact on gynecomastia outcomes cannot be overemphasized, as factors such as diet, exercise, and substance use significantly influence post-surgical results.
Risk Factors for Gynecomastia Recurrence
Understanding the answer to “does gynecomastia come back after surgery” helps patients focus on realistic outcomes and preventable risks.
Most patients do not experience recurrence. However, those with persistent risk factors may notice changes over time.
Addressing these proactively is the best way to maintain your post-gynecomastia surgical result.
Weight Gain and Fat Redistribution in the Chest
If you are wondering does gynecomastia come back after surgery due to weight gain, the answer is no—however, fat gain can mimic the appearance but is not true recurrence.
After surgery, excessive weight gain can lead to fat accumulation in the chest area. This condition is called pseudogynecomastia.
While this is not a return of breast gland tissue, it can cause a similar appearance. Patients should aim to maintain a stable weight to prevent fat redistribution.
Use of Testosterone Boosters or Steroids Post-Surgery
Many patients mistakenly assume that testosterone supplements will prevent recurrence.
In reality, some testosterone-boosting substances are converted into estrogen within the body, particularly when not medically supervised. This can cause breast tissue growth and the return of your gynecomastia.
Anabolic steroid use is a well-known contributor to gynecomastia and should be avoided entirely.
Endocrine Disorders or Uncontrolled Hormone Levels
Undiagnosed or unmanaged hormonal disorders can increase the chance of recurrence.
Annual physical exams and hormone testing may be recommended for patients with a history of hormone imbalance.
Early intervention allows patients to avoid triggering new breast tissue growth.
How to Maintain Results After Gynecomastia Surgery

Understanding how to maintain results after gynecomastia surgery involves adhering to postoperative instructions and making long-term health-conscious decisions.
For most patients, the results of gynecomastia surgery are permanent—if they maintain a healthy lifestyle and avoid known triggers. Following a few simple habits can make a significant difference in sustaining the outcome.
Most patients achieve permanent results from gynecomastia surgery, provided the underlying hormonal or lifestyle causes are no longer present.
Following Postoperative Guidelines from Your Plastic Surgeon
Every patient receives specific instructions for recovery.
These may include wearing a compression garment, avoiding strenuous activities, and caring for the surgical incision.
Adhering to these guidelines supports proper healing and reduces the chance of complications.
Maintaining a Stable Weight and Body Composition
Postoperative results are best preserved when patients maintain a stable weight.
Regular cardiovascular and strength-training exercises support healthy hormone levels and body fat distribution.
Nutritional balance is equally important in maintaining a stable healthy weight.
Avoiding Substances Known to Trigger Gland Growth
Patients should avoid steroids, excessive alcohol, marijuana, and any over-the-counter supplements that claim to boost testosterone.
Many of these products alter hormone levels in unpredictable ways and can lead to breast gland stimulation.
When to Consider Revision Surgery
Revision surgery for gynecomastia may be necessary in a small number of patients who experience incomplete correction or contour irregularities.
Although uncommon, revision surgery may be appropriate if a patient notices residual fullness, asymmetry, or other cosmetic concerns. These procedures are usually less extensive than the original surgery and are targeted to correct a specific issue.
Signs That May Indicate a Need for Revision
Visible lumps beneath the nipple, uneven chest contour, or recurrence of firmness in the chest may warrant reevaluation.
Patients should wait until full healing has occurred before making any decisions about revision.
Evaluation Timeline After Initial Healing
It typically takes several months for swelling to fully subside and final results to appear.
Most plastic surgeons recommend waiting at least six months before evaluating for revision. Follow-up appointments are important during this time.
Techniques Used in Gynecomastia Revision Surgery
Revision may involve removal of residual gland tissue, contour liposuction or skin removal..
Each case is assessed individually and the surgical plan is customized based on the patient’s chest appearance and goals.
Long-Term Results and Patient Outlook
The long-term outlook after male breast reduction is highly favorable, especially in patients who maintain a healthy weight and avoid known risk factors.
When performed by an experienced plastic surgeon and followed by appropriate lifestyle management, the long-term outlook for gynecomastia surgery is overwhelmingly positive.
Patients often report significant improvements in confidence and body image.
What Most Patients Can Expect Years Later
Most patients maintain a flatter, firmer chest for years that looks normal and masculine.
Recurrence is rare when hormonal balance is stable and healthy habits are maintained. The surgical incision typically heals with minimal visibility.
Monitoring for Subtle Changes in Chest Contour
Patients should remain aware of any changes in their chest appearance, such as increased fullness, tenderness, or visible asymmetry.
Early detection of issues allows for easier intervention if needed.
Role of Annual Physical Exams and Blood Work
Routine health evaluations can help identify hormonal imbalances or other changes that may affect long-term results.
Blood work, including hormone panels, may be especially valuable for patients with a history of endocrine disorders.
If the question “does gynecomastia come back after surgery” still remains, scheduling a consultation will help clarify your personal risks and outcomes.
Schedule a Personalized Consultation with Dr. Adrian Lo

If you are concerned about the possibility of gynecomastia returning after surgery—or if you are considering male breast reduction for the first time—Dr. Adrian Lo offers expert evaluation and surgical care.
With years of experience serving patients throughout Pennsylvania, New Jersey, and Delaware, Dr. Lo customizes each surgical plan to address your unique anatomy, health background, and aesthetic goals.
A consultation provides a clear understanding of what to expect, how to maintain results, and what can be done if revision is needed.
Contact us today to begin the conversation about restoring your confidence and achieving long-term results.
